Moxa: what it is
Moxibustion, also called moxa, is a therapeutic technique that comes from the east.
It is based on the principles of Traditional Chinese Medicine, imported and reviewed from Japan in the form we know today.
Japanese culture has made changes in the form and application of Chinese medicine, but the concepts and postulates are original.
Massage, acupuncture, moxa, cupping, the use of certain herbs, up to nutrition, plus other therapeutic techniques, act on the energy meridians, in which, according to Traditional Chinese Medicine, vital energy flows, the Qi .
The harmony of the flow of Qi within the Meridian circulation generates health, the obstruction or "vice" of Qi generates the disease instead.
Traditional Chinese Medicine therefore acts to rebalance the circulation of Qi, regulating the Yin and Yang within the body.
Moxa is one of the methods used to rebalance the body and bring physical and mental health and well-being.
Moxa consists of applying heat to the meridian points, mainly to tone and stimulate the circulation of Qi.
In some cases, although it consists of applying heat, moxa can also be used to disperse energy stagnation on the points, even in the case of application on pain points (ashi points).
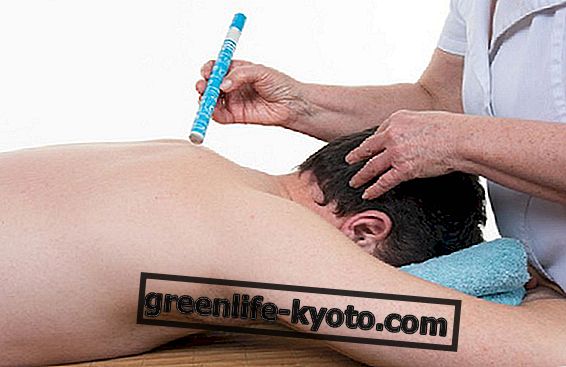
The heat can be applied by artemisia vulgaris cones, which are burned, or by incandescent cigars, depending on the type of moxa treatment, Chinese or Japanese, used.
Chinese moxa and Japanese moxa: differences
Both types of moxa are based on the knowledge and treatment of acupuncture meridian points and traditional Chinese medicine concepts.
Both techniques consist of applying heat but there are slight differences between Chinese moxa and Japanese moxa.
Simplifying, and without going into the specifics of Traditional Chinese Medicine, it can be observed that Japanese moxa applies moxa with a more pronounced energy intent than Chinese moxa: the application of heat is in fact performed on precise acupoints by burning small cones of artemisia, directly in contact with the skin.
A good operator is able, both for the size of the cones (the size of a grain of rice ) and for their specific abilities, to prevent the skin from burning, and to optimize the energetic action on the point, thanks to the accuracy of its location.
In some cases, such as for prolonged treatments of greater intensity, a small thin disc of ginger or potatoes is superimposed, in order to transmit the heat without going to damage the skin and, in the case of ginger, to amplify the skin. tonic action of the treatment.
In Chinese moxa, on the other hand, it is used to heat the point using artemisia cigars or other cigars with the same punctual heating capacity, without however coming into contact with the skin, therefore at a distance.
This allows a more generalized work on the energy channel and less precise on the acupoint, and acts on a physical rather than an energetic level, and is especially useful on the ashi points, which are the pain points, often located outside the energy channels.
The Chinese moxa has the advantage, but also the limit, of being able to facilitate the application and to act on a more superficial level, in case of invasion of cold and wind energies, muscular contractions, in case of stagnation of mucus, as for the sinusitis, to "dissolve" in all those situations in which there is something contracted due to a stagnation of yin energy, since the heat, which is yang, its opposite and complementary, expands.
There is also a particular type of moxa which involves combining moxa with acupuncture, and which must be under medical supervision, since its action is very strong and precise.













