The use of salt in the kitchen dates back to ancient times, when our ancestors discovered that its use could enhance the flavors of the dishes, and preserve food . It was so important that the ancient Romans built the Via Salaria, in order to supply themselves with salt from the Adriatic Sea. Its name, in fact, unlike all the other consular offices that are named for the maker of their construction, derives directly from the essential use made of it: we are talking about transporting salt from the Campus salinarum to Fiumicino and Maccarese.
Salt was such an important element in the economies of the countries that even between 1482 and 1699, the possession of this substance and the related taxes applied to its trade were the cause of popular uprisings and conflicts between the various powers, dominant in Europe. These war events became known as the "Salt War".
Today we use it in the kitchen to season food or to preserve it in a natural way, through the process of brine, which exploits the dehydrating power that salt has on the substances with which it comes into contact, from which it extracts water by osmosis .
What is salt
The common table salt is sodium chloride or the sodium salt of hydrochloric acid. At room temperature it appears as a crystalline solid, colorless and with a characteristic smell and taste . In general, sodium chloride is essential for life on Earth. Most tissues and fluids of living things contain some amount of this mineral. Sodium ions are essential for the transmission of sensory and motor signals along the nervous system. An aqueous solution containing 0.9% sodium chloride is called " physiological solution " because it has the same osmotic pressure as the human blood plasma, and is therefore used in medicine to cure dehydration . However, recent studies have shown that a dose higher than 5g / day can be very harmful, leading to a 27% increase in the incidence of stroke or cardiovascular disease .
Unfortunately, the usual table salt has nothing to do with salt in its natural state, as the processes of refining and bleaching impoverish it of the precious substances it contains. Natural salt, in fact that produced by solar evaporation of sea water (unpolluted) is a compound more or less balanced in its structure: in addition to sodium chloride there are magnesium chloride, magnesium sulfate, calcium sulfate, sulphate of potassium, calcium carbonate, bromine and iodine. Furthermore we also find traces of all known minerals such as boron, barium, silicon, fluorine, lithium, manganese, zinc, phosphorus, copper, silver, etc. which allow our body to function optimally.
With the industrial process the salt is chemically cleaned and reduced to sodium chloride, about 95% ; the essential minerals and trace elements are simply considered as 'impurities' and as such are eliminated, even if they are the same ones that constitute and allow the proper functioning of our body.
The use of salt in the kitchen
In the kitchen the use of salt serves primarily to enhance the flavor of food, which is why its use is found in all known culinary traditions as well as being widely exploited in the food industry both as an ingredient and as a means of storing food.
Brine is a simple method to preserve food, which uses a more or less concentrated solution of water and salt, whose osmotic effect preserves food from the putrefaction caused by bacteria, because it inhibits their development and proliferation.
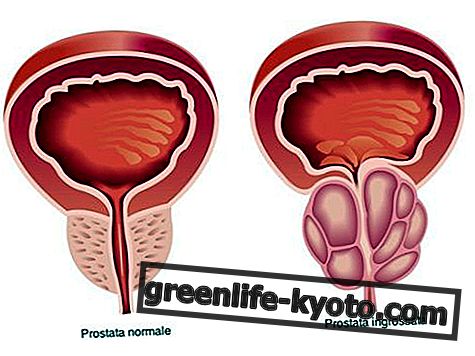
Furthermore, kitchen salt with special elements is normally prescribed to cure or prevent some diseases (for example iodized salt for hypothyroidism or added potassium chloride for hypertension ). However, sodium retains the liquids, making it the main responsible for water retention and everything that can come from cellulite to high blood pressure.
Salt production
Salt is found abundantly in nature: most of it is dissolved in water, to form sea water ; in part it is found as a mineral in the solid state in deposits on land (in this case it is called " rock salt ").
Production processes vary depending on the form in which the salt is available. In Italy, the largest salt pans are found in Margherita di Savoia, in Puglia ; in Cervia in Romagna ; near Cagliari, in Sardinia; and in Trapani, Sicily, where sea salt is included among the traditional Sicilian food products, recognized by the Ministry of Agricultural, Food and Forestry Policies.
The types of salt
The main salts for use in the kitchen easily available on the market are:
- Salt of rock salt : fine or coarse, it is the one with a higher percentage of sodium chloride, reaching a value of 99.5%. It is extracted by drilling from huge underground deposits where the mineral settled when the current Sicily was still partly covered by the sea, several million years ago.
- Sea salt: obtained in the salt pans, by evaporation of sea water, it is then refined to eliminate impurities, but often this treatment also leads to a partial elimination of the minerals that compose it, impoverishing it of precious nutrients. In addition, chemical anti-caking agents are often added to prevent hardening by absorbing moisture.
- Iodized salt : consists of refined salt to which small amounts of iodine have been added (note the inconsistency: the refining industry eliminates the iodine present naturally in the crude salt, then adds it to the refined one). Iodized salt is recommended to prevent thyroid deficiency due to iodine deficiency.
- Whole gray salt : also known as the fleur de sel (the salt flower), it is a type of raw salt, produced in the Atlantic north of France, in southern Brittany. The characteristic of this product is that of not being refined, so as to preserve the clay particles in suspension at the time of collection, as well as the scent and taste of the Dunaliella Salina alga, present in the ocean waters. It gives flavors a salty but very delicate taste, does not cover food but enhances their natural flavor, because it contains less sodium chloride to the advantage of other precious minerals, is rich in magnesium, potassium, calcium, iodine and other trace elements and more poor in sodium compared to normal refined white salt. Therefore it is indicated for a healthier diet and for those suffering from high blood pressure . Rich in flavor but not too salty, this condiment is perfect for any type of cuisine. It can be used both in pasta cooking water and to dress vegetables and salads meats and fish.
- Himalayan pink salt: formed in the secondary era more than 200 million years ago, this ancient salt is harvested by hand and has always been known and used in the East for its particular characteristics and properties, as it contains pure minerals and trace elements essential (calcium, potassium, zinc, copper, sulfur, iron, etc., ). Particularly suitable for food use, this salt has a rounder, less aggressive taste, so as not to cover the flavors of other foods, but accompanies them and enhances them; it is completely assimilable by the intestine, which does not have to split it into smaller parts, but manages to digest it immediately; and thanks to the other minerals (as many as 84), it is already complete, remineralizing without causing any water retention.